using Couchbase.Extensions.Caching;
using Couchbase.Extensions.DependencyInjection;Distributed caching with ASP.NET Core and Couchbase
This is a repost that originally appeared on the Couchbase Blog: Distributed caching with ASP.NET Core and Couchbase.
Distributed caching can help to improve performance of an ASP.NET Core application. This is especially true for an ASP.NET application that’s deployed to a server farm or scalable cloud environment. Using Couchbase Server for caching is one of the many features that make it an ideal choice for your engagement database needs.
In this blog post, I’ll show you how to use the Couchbase.Extensions.Caching middleware plugin to easily add distributed caching capabilities to your application.
You can follow along with the sample code I wrote for this post on GitHub.
Please note that Couchbase.Extensions.Caching is currently in a beta2 release (as I’m writing this blog post), so some things may change.
Basic setup of Couchbase
First, you’ll need a Couchbase Server cluster running (you can install it on-premise, or with Docker, or even in Azure if you’d like).
Next, you’ll need to create a bucket in Couchbase where cached data will be stored. I called mine "cachebucket". You may want to take advantage of the new ephemeral bucket feature in Couchbase Server 5.0 for caching, but it is not required.
If you are using Couchbase Server 5.0, you’ll also need to create a user with permissions (Data Writer and Data Reader) on that bucket. To keep things simple, create a user that has the same name as the bucket (e.g. "cachebucket").
Distributed Caching with Couchbase.Extensions
The Couchbase.Extensions (GitHub) project aims to make working with Couchbase Server and .NET Core simpler. Caching is just one of these extensions.
You can add it to your ASP.NET Core project with NuGet, via Package Manager: Install-Package Couchbase.Extensions.Caching -Version 1.0.0-beta2, or with the NuGet UI, or you can use the .NET command line: dotnet add package Couchbase.Extensions.Caching --version 1.0.0-beta2.
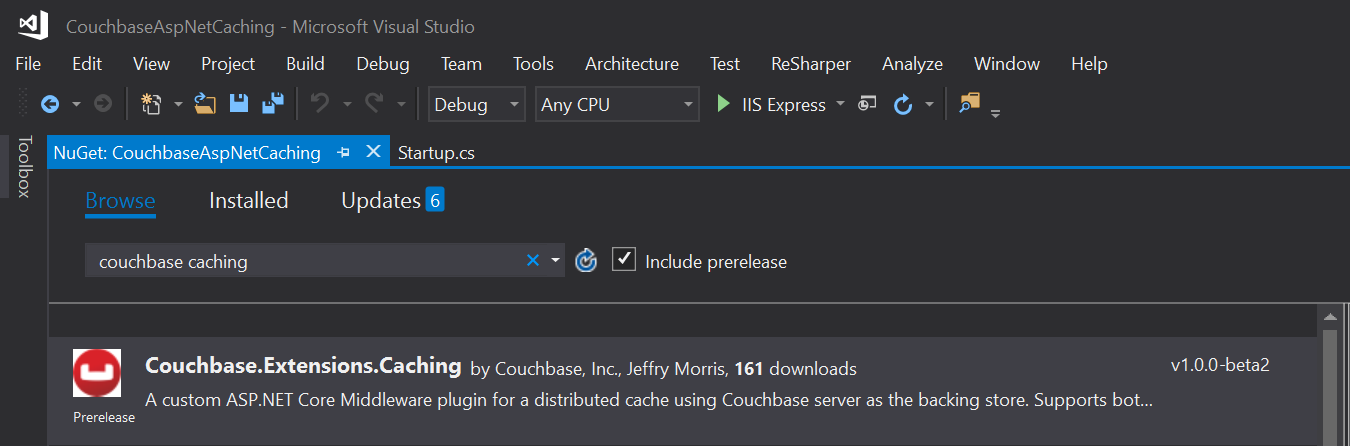
Once you’ve added this to your project, you’ll need to make a couple minor changes to your Startup class in Startup.cs.
First, in ConfigureServices, add a couple namespaces:
This will make the Caching namespace available, and specifically the AddDistributedCouchbaseCache extension method for IServiceCollection. Next, call that extension method from within the ConfigureServices method.
The other namespace in there, DependencyInjection, is necessary to inject Couchbase functionality. In this case, it’s going to be used only by the Caching extension. But you can use it for other purposes too, which I will cover in a future blog post.
But for now, it’s just needed for the AddCouchbase extension method on IServiceCollection.
Finally, put them both together, and your ConfigureServices method should look like this:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
services.AddCouchbase(opt =>
{
opt.Servers = new List<Uri>
{
new Uri("http://localhost:8091")
};
});
services.AddDistributedCouchbaseCache("cachebucket", "password", opt => { });
}Using distributed caching
Now that you have distributed caching setup with Couchbase in your ASP.NET Core project, you can use IDistributedCache elsewhere in your project.
Injecting IDistributedCache
A simple example would be to use it directly in a controller. It can be injected into constructors as you need it:
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IDistributedCache _cache;
public HomeController(IDistributedCache cache)
{
_cache = cache;
}
// ... snip ...
}Caching strings
You can use the GetString and SetString methods to retrieve/set a string value in the cache.
// cache/retrieve from cache
// a string, stored under key "CachedString1"
var message = _cache.GetString("CachedString1");
if (message == null)
{
message = DateTime.Now + " " + Path.GetRandomFileName();
_cache.SetString("CachedString1", message);
}
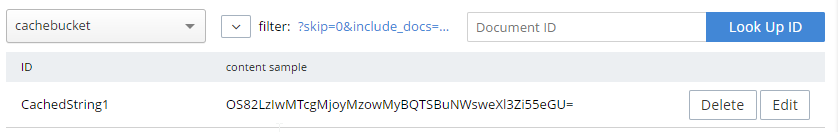
ViewData["Message"] = "'CachedString1' is '" + message + "'";This would appear in the "cachebucket" bucket as an encoded binary value (not JSON).
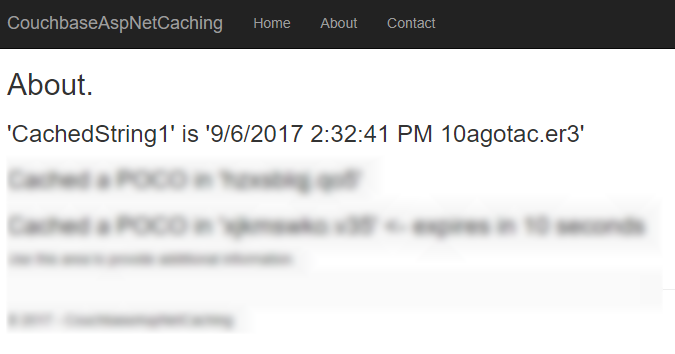
In the sample code, I simply print out the ViewData["Message"] in the Razor view. It should look something like this:
Caching objects
You can also use Set<> and Get<> methods to save and retrieve objects in the cache. I created a very simple POCO (Plain Old CLR Object) to demonstrate:
public class MyPoco
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int ShoeSize { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}Next, in the sample, I generate a random string to use as a cache key, and a random generated instance of MyPoco. First, I store them in the cache using the Set<> method:
var pocoKey = Path.GetRandomFileName();
_cache.Set(pocoKey, MyPoco.Generate(), null);
ViewData["Message2"] = "Cached a POCO in '" + pocoKey + "'";Then, I print out the key to the Razor view:
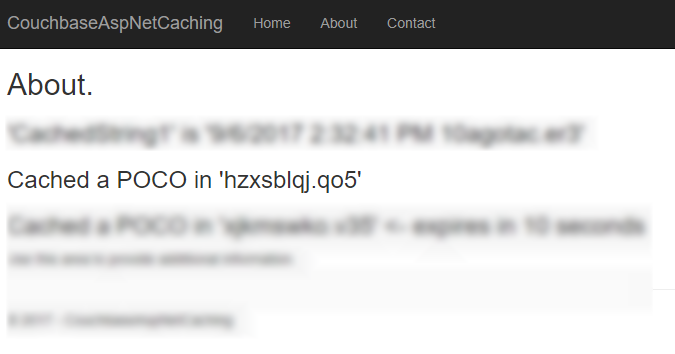
Next, I can use this key to look up the value in Couchbase:
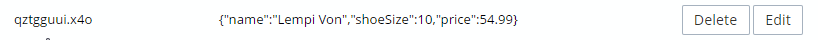
Also, notice that it’s been serialized to JSON. This not only means that you can read it, but you can also query it with N1QL (if you need to).
Distributed caching with expiration
If you want the values in the cache to expire after a certain period of time, you can specify that with DistributedCacheEntryOptions (only SlidingExpiration is supported at this time).
var anotherPocoKey = Path.GetRandomFileName();
_cache.Set(anotherPocoKey, MyPoco.Generate(), new DistributedCacheEntryOptions
{
SlidingExpiration = new TimeSpan(0, 0, 10) // 10 seconds
});
ViewData["Message3"] = "Cached a POCO in '" + anotherPocoKey + "'";In the sample project, I’ve also set this to print out to Razor.
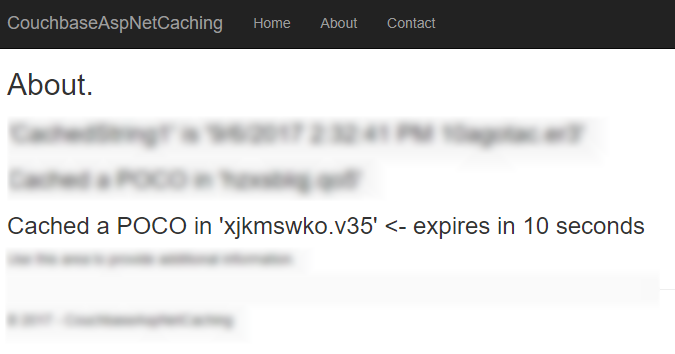
If you view that document (before the 10 seconds runs out) in Couchbase Console, you’ll see that it has an expiration value in its metadata. Here’s an example:
{
"id": "xjkmswko.v35",
"rev": "1-14e1d9998125000059b0404502000001",
"expiration": 1504723013,
"flags": 33554433
}After 10 seconds, that document will be gone from the bucket, and you’ll see an error "not found (Document does not exist)".
Tearing down distributed caching
Finally, don’t forget to cleanup the resources used by the Couchbase .NET SDK for distributed caching. One easy way to do this is with the ApplicationStopped event. You can wire this up in Startup:
appLifetime.ApplicationStopped.Register(() =>
{
app.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<ICouchbaseLifetimeService>().Close();
});Note that you will have to add IApplicationLifetime appLifetime as a parameter to the Configure method in Startup if you haven’t already.
Summary
Using Couchbase Server for distributed caching in your ASP.NET Core application is a great way to improve performance and scalability in your application. These kind of "engagement" use cases are what Couchbase Server excels at. To see customers that are using Couchbase Server for caching, check out the Couchbase Customers page.
If you have questions or comments about the Couchbase.Extensions.Caching project, make sure to check out the GitHub repository or the Couchbase .NET SDK forums.
As always, you can reach me by leaving a comment below or finding me on Twitter @mgroves.
