public class ShoppingCartMigrator
{
readonly IBucket _bucket;
readonly SqlToCbContext _context;
public ShoppingCartMigrator(IBucket bucket, SqlToCbContext context)
{
_bucket = bucket;
_context = context;
}
}Posts tagged with '.net'
- Data modeling
- The data itself (this blog post)
- Applications using the data
Data Types in JSON vs SQL
| SQL Server | JSON |
|---|---|
|
nvarchar, varchar, text |
string |
|
int, float, decimal, double |
number |
|
bit |
boolean |
|
null |
null |
|
XML/hierarchyid fields |
array / object |
Migrating and translating data
- Give yourself plenty of time in planning. While migrating, you may discover that you need to rethink your model. You will need to test and make adjustments, and it’s better to have extra time than make mistakes while hurrying. Migrating data is an iterative cycle: migrate a table, see if that works, adjust, and keep iterating. You may have to go through this cycle many times.
- Test your migration using real data. Data can be full of surprises. You may think that NVARCHAR field only ever contains string representations of numbers, but maybe there are some abnormal rows that contain words. Use a copy of the real data to test and verify your migration.
- Be prepared to run the migration multiple times. Have a plan to cleanup a failed migration and start over. This might be a simple
DELETE FROM bucketin N1QL, or it could be a more nuanaced and targeted series of cleanups. If you plan from the start, this will be easier. Automate your migration, so this is less painful. - ETL or ELT? Extract-Transform-Load, or Extract-Load-Transform. When are you going to do a transform? When putting data into Couchbase, the flexibility of JSON allows you to transfer-in-place after loading if you choose.
An example ETL migration
ShoppingCartMigrator class and a SocialMediaMigrator class. I’m only going to cover the shopping cart in this post. I pass it a Couchbase bucket and the Entity Framework context that I used in the last blog post. (You could instead pass an NHibernate session or a plain DbConnection here, depending on your preference).Go method to perform the migration, and a Cleanup method to delete any documents created in the migration, should I choose to.Go method, I let Entity Framework do the hard work of the joins, and loop through every shopping cart.public bool Go()
{
var carts = _context.ShoppingCarts
.Include(x => x.Items)
.ToList();
foreach (var cart in carts)
{
var cartDocument = new Document<dynamic>
{
Id = cart.Id.ToString(),
Content = MapCart(cart)
};
var result = _bucket.Insert(cartDocument);
if (!result.Success)
{
Console.WriteLine($"There was an error migrating Shopping Cart {cart.Id}");
return false;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Successfully migrated Shopping Cart {cart.Id}");
}
return true;
}public void Cleanup()
{
Console.WriteLine("Delete all shopping carts...");
var result = _bucket.Query<dynamic>("DELETE FROM `sqltocb` WHERE type='ShoppingCart';");
if (!result.Success)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{result.Exception?.Message}");
Console.WriteLine($"{result.Message}");
}
}DELETE FROM sqltocb WHERE fingerprint = '999cfbc3-186e-4219-ab5d-18ad130a9dc6'). Or vice versa: fingerprint the problematic data for later analysis and delete the rest. Just make sure to cleanup these temporary fields when the migration is completed successfully.What about the other features of SQL Server?
- SQL/N1QL
- Stored Procedures
- Service tiers
- Triggers
- Views
- Serialization
- Security
- Concurrency
- Autonumber
- OR/Ms and ODMs
- Transactions
Summary
This is a repost that originally appeared on the Couchbase Blog: Moving from SQL Server to Couchbase Part 1: Data Modeling.
In this series of blog posts, I’m going to lay out the considerations when moving to a document database when you have a relational background. Specifically, Microsoft SQL Server as compared to Couchbase Server.
In three parts, I’m going to cover:
-
Data modeling (this blog post)
-
The data itself
-
Applications using the data
The goal is to lay down some general guidelines that you can apply to your application planning and design.
If you would like to follow along, I’ve created an application that demonstrates Couchbase and SQL Server side-by-side. Get the source code from GitHub, and make sure to download a developer preview of Couchbase Server.
Why would I do this?
Before we get started, I want to spend a little bit of time on motivation. There are 3 main reasons why one might consider using a document data store instead of (or in addition to) a relational database. Your motivation may be one or all three:
-
Speed: Couchbase Server uses a memory-first architecture which can provide a great speed boost as compared to a relational databases
-
Scalability: Couchbase Server is a distributed database, which allows you to scale out (and scale back in) capacity by just racking up commodity hardware. Built-in Couchbase features like auto-sharding, replication, load balancing make scaling a lot smoother and easier than relational databases.
-
Flexibility: Some data fits nicely in a relational model, but some data can benefit from the flexibility of using JSON. Unlike SQL Server, schema maintenance is no longer an issue. With JSON: the schema bends as you need it to.
For these reasons and others, Gannett switched from SQL Server to Couchbase Server. If you are considering this, definitely check out Gannett’s full presentation.
It should be noted that document databases and relational databases can be complimentary. Your application may be best served by one, the other, or a combination of both. In many cases, it simply is not possible to completely remove relational databases from your design, but a document database like Couchbase Server can still bring the above benefits to your software. The rest of this blog series will assume you have a SQL Server background and are either replacing, supplimenting, or starting a new greenfield project using Couchbase.
The ease or difficulty of transitioning an existing application varies widely based on a number of factors. In some cases it may be extremely easy; in some cases it will be time-consuming and difficult; in some (shrinking number of) cases it may not even be a good idea.
Understanding the differences
The first step is to understand how data is modeled in a document database. In a relational database, data is typically stored flat in a table and it is given structure with primary and foreign keys. As a simple example, let’s consider a relational database for a web site that has a shopping cart as well as social media features. (In this example, those features are unrelated to keep things simple).
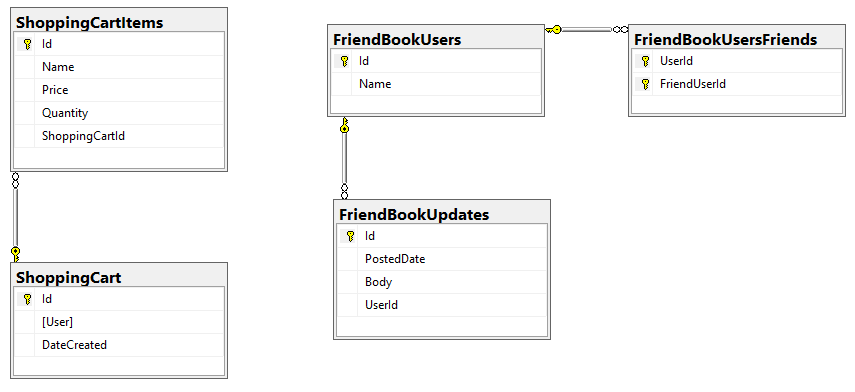
In a document database, data is stored as keys and values. A Couchbase bucket contains documents; each document has a unique key and a JSON value. There are no foreign keys (or, more accurately, there are no foreign key constraints).
Here’s a high-level comparison of SQL Server features/naming as compared to Couchbase:
| SQL Server | Couchbase Server |
|---|---|
|
Server |
Cluster |
|
Database |
Bucket |
|
Row(s) from table(s) |
Document |
|
Column |
JSON key/value |
|
Primary Key |
Document Key |
These comparisons are a metaphorical starting point. Looking at that table, it might be tempting to take a simplistic approach. "I have 5 tables, therefore I’ll just create 5 different types of documents, with one document per row." This is the equivalent of literally translating a written language. The approach may work sometimes, but it doesn’t take into account the full power of a document database that uses JSON. Just as a literal translation of a written language doesn’t take into account cultural context, idioms, and historical context.
Because of the flexibility of JSON, the data in a document database can be structured more like a domain object in your application. Therefore you don’t have an impedence mismatch that is often addressed by OR/M tools like Entity Framework and NHibernate.
There are two main approaches you can use when modeling data in Couchbase that we will examine further:
-
Denormalization - Instead of splitting data between tables using foreign keys, group concepts together into a single document.
-
Referential - Concepts are given their own documents, but reference other documents using the document key.
Denormalization example
Let’s consider the "shopping cart" entity.
To represent this in a relational database would likely require two tables: a ShoppingCart table and a ShoppingCartItem table with a foreign key to a row in ShoppingCart.
When creating the model for a document database, the decision has to be made whether to continue modeling this as two separate entities (e.g. a Shopping Cart document and corresponding Shopping Cart Item documents) or whether to "denormalize" and combine a row from ShoppingCart and row(s) from ShoppingCartItem into a single document to represent a shopping cart.
In Couchbase, using a denormalization strategy, a shopping cart and the items in it would be represented by a single document.
{
"user": "mgroves",
"dateCreated": "2017-02-02T15:28:11.0208157-05:00",
"items": [
{
"name": "BB-8 Sphero",
"price": 80.18,
"quantity": 1
},
{
"name": "Shopkins Season 5",
"price": 59.99,
"quantity": 2
}
],
"type": "ShoppingCart"
}Notice that the relationship between the items and the shopping cart is now implicit to being contained in the same document. No more need for an ID on the items to represent a relationship.
In C#, you would likely define ShoppingCart and Item classes to model this data:
public class ShoppingCart
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string User { get; set; }
public DateTime DateCreated { get; set; }
public List<Item> Items { get; set; }
}
public class Item
{
public Guid Id { get; set; } // necessary for SQL Server, not for Couchbase
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
}These classes would still make sense with Couchbase, so you can reuse them or design them this way. But with a relational database, this design does not match up in a direct way.
Hence the need for OR/Ms like NHibernate or Entity Framework. The way the above model can be mapped to a relational database is represented in Entity Framework* like this:
public class ShoppingCartMap : EntityTypeConfiguration<ShoppingCart>
{
public ShoppingCartMap()
{
this.HasKey(m => m.Id);
this.ToTable("ShoppingCart");
this.Property(m => m.User);
this.Property(m => m.DateCreated);
this.HasMany(m => m.Items)
.WithOptional()
.HasForeignKey(m => m.ShoppingCartId);
}
}
public class ShoppingCartItemMap : EntityTypeConfiguration<Item>
{
public ShoppingCartItemMap()
{
this.HasKey(m => m.Id);
this.ToTable("ShoppingCartItems");
this.Property(m => m.Name);
this.Property(m => m.Price);
this.Property(m => m.Quantity);
}
}*Other OR/Ms will have similar mappings
Based on these mappings and an analysis of the use cases, I could decide that it would be modeled as a single document in Couchbase. ShoppingCartItemMap only exists so that the OR/M knows how to populate the Items property in ShoppingCart. Also, it’s unlikely that the application will be doing reads of the shopping cart without also needing to read the items.
In a later post, OR/Ms will be discussed further, but for now I can say that the ShoppingCartMap and ShoppingCartItemMap classes are not necessary when using Couchbase, and the Id field from Item isn’t necessary. In fact, the Couchbase .NET SDK can directly populate a ShoppingCart object without an OR/M in a single line of code:
public ShoppingCart GetCartById(Guid id)
{
return _bucket.Get<ShoppingCart>(id.ToString()).Value;
}This isn’t to say that using Couchbase will always result in shorter, easier to read code. But for certain use cases, it can definitely have an impact.
Referential example
It’s not always possible or optimal to denormalize relationships like the ShoppingCart example. In many cases, a document will need to reference another document. Depending on how your application expects to do reads and writes, you may want to keep your model in separate documents by using referencing.
Let’s look at an example where referencing might be the best approach. Suppose your application has some social media elements. Users can have friends, and users can post text updates.
One way to model this:
-
Users as individual documents
-
Updates as individual documents that reference a user
-
Friends as an array of keys within a user document
With two users, two updates, we would have 4 documents in Couchbase that look like this:
[
// Key: "7fc5503f-2092-4bac-8c33-65ef5b388f4b"
{
"friends": [
"c5f05561-9fbf-4ab0-b68f-e392267c0703"
],
"name": "Matt Groves",
"type": "User"
},
// Key: "c5f05561-9fbf-4ab0-b68f-e392267c0703"
{
"friends": [ ],
"name": "Nic Raboy",
"type": "User"
},
// Key: "5262cf62-eb10-4fdd-87ca-716321405663"
{
"body": "Nostrum eligendi aspernatur enim repellat culpa.",
"postedDate": "2017-02-02T16:19:45.2792288-05:00",
"type": "Update",
"user": "7fc5503f-2092-4bac-8c33-65ef5b388f4b"
},
// Key: "8d710b83-a830-4267-991e-4654671eb14f"
{
"body": "Autem occaecati quam vel. In aspernatur dolorum.",
"postedDate": "2017-02-02T16:19:48.7812386-05:00",
"type": "Update",
"user": "c5f05561-9fbf-4ab0-b68f-e392267c0703"
}
]I decided to model 'friends' as a one-way relationship (like Twitter) for this example, which is why Matt Groves has Nic Raboy as a friend but not vice-versa. (Don’t read too much into this, Nic :).
The way to model this in C# could be:
public class FriendbookUser
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual List<FriendbookUser> Friends { get; set; }
}
public class Update
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public DateTime PostedDate { get; set; }
public string Body { get; set; }
public virtual FriendbookUser User { get; set; }
public Guid UserId { get; set; }
}The Update to FriendbookUser relationship can be modeled as either a Guid or as another FriendbookUser object. This is an implementation detail. You might prefer one, the other, or both, depending on your application needs and/or how your OR/M works. In either case, the underlying model is the same.
Here’s the mapping I used for these classes in Entity Framework. Your mileage may vary, depending on how you use EF or other OR/M tools. Focus on the underlying model and not the details of the OR/M mapping tool.
public class UpdateMap : EntityTypeConfiguration<Update>
{
public UpdateMap()
{
this.HasKey(m => m.Id);
this.ToTable("FriendBookUpdates");
this.Property(m => m.Body);
this.Property(m => m.PostedDate);
this.HasRequired(m => m.User)
.WithMany()
.HasForeignKey(m => m.UserId);
}
}
public class FriendbookUserMap : EntityTypeConfiguration<FriendbookUser>
{
public FriendbookUserMap()
{
this.HasKey(m => m.Id);
this.ToTable("FriendBookUsers");
this.Property(m => m.Name);
this.HasMany(t => t.Friends)
.WithMany()
.Map(m =>
{
m.MapLeftKey("UserId");
m.MapRightKey("FriendUserId");
m.ToTable("FriendBookUsersFriends");
});
}
}If, instead of storing these entities as separate documents, we applied the same denormalization as the shopping cart example and attempted to store a user and updates in one document, we would end up with some problems.
-
Duplication of friends: each user would store the details for their friends. This is not tenable, because now a user’s information would be stored in multiple places instead of having a single source of truth (unlike the shopping cart, where having the same item in more than one shopping cart probably doesn’t make any domain sense). This might be okay when using Couchbase as a cache, but not as a primary data store.
-
Size of updates: Over a period of regular use, an individual user could post hundreds or thousands of updates. This could lead to a very large document which could slow down I/O operations. This can be mitigated with Couchbase’s sub-document API, but also note that Couchbase has a ceiling of 20mb per document.
Note: There’s an N+1 problem here too (friends of friends, etc), but I’m not going to spend time on addressing that. It’s a problem that’s not unique to either database.
Additionally, it may not be the case that when the application reads or writes a user that it will need to read or write friends & updates. And, when writing an update, it’s not likely that the application will need to update a user. Since these entities may often be read/written on their own, that indicates that they need to be modeled as separate documents.
Note the array in the Friends field in the user document and the value in the User field in the update document. These values can be used to retrieve the associated documents. Later in this post, I’ll discuss how to do it with key/value operations and how to do it with N1QL.
To sum up, there are two ways to model data in a document database. The shopping cart example used nested objects, while the social media example used separate documents. In those examples, it was relatively straightforward to choose. When you’re making your own modeling decisions, here’s a handy cheat sheet:
| If … | Then consider… |
|---|---|
|
Relationship is 1-to-1 or 1-to-many |
Nested objects |
|
Relationship is many-to-1 or many-to-many |
Separate documents |
|
Data reads are mostly parent fields |
Separate document |
|
Data reads are mostly parent + child fields |
Nested objects |
|
Data reads are mostly parent or child (not both) |
Separate documents |
|
Data writes are mostly parent and child (both) |
Nested objects |
Key/value operations
To get document(s) in Couchbase, the simplest and fastest way is to ask for them by key. Once you have one of the FriendbookUser documents above, you can then execute another operation to get the associated documents. For instance, I could ask Couchbase to give me the documents for keys 2, 3, and 1031 (as a batch operation). This would give me the documents for each friend. I can then repeat that for Updates, and so on.
The benefit to this is speed: key/value operations are very fast in Couchbase, and you will likely be getting values directly from RAM.
The drawback is that it involves at least two operations (get FriendbookUser document, then get the Updates). So this may involve some extra coding. It may also require you to think more carefully about how you construct document keys (more on that later).
N1QL
In Couchbase, you have the ability to write queries using N1QL, which is SQL for JSON. This includes the JOIN keyword. This allows me to, for instance, write a query to get the 10 latest updates and the users that correspond to them.
public List<Update> GetTenLatestUpdates()
{
var n1ql = @"SELECT up.body, up.postedDate, { 'id': META(u).id, u.name} AS `user`
FROM `sqltocb` up
JOIN `sqltocb` u ON KEYS up.`user`
WHERE up.type = 'Update'
ORDER BY STR_TO_MILLIS(up.postedDate) DESC
LIMIT 10;";
var query = QueryRequest.Create(n1ql);
query.ScanConsistency(ScanConsistency.RequestPlus);
var result = _bucket.Query<Update>(query);
return result.Rows;
}The result of this query would be:
[
{
"body": "Autem occaecati quam vel. In aspernatur dolorum.",
"postedDate": "2017-02-02T16:19:48.7812386-05:00",
"user": {
"id": "c5f05561-9fbf-4ab0-b68f-e392267c0703",
"name": "Bob Johnson"
}
},
{
"body": "Nostrum eligendi aspernatur enim repellat culpa eligendi maiores et.",
"postedDate": "2017-02-02T16:19:45.2792288-05:00",
"user": {
"id": "7fc5503f-2092-4bac-8c33-65ef5b388f4b",
"name": "Steve Oberbrunner"
}
},
// ... etc ...
]N1QL allows you to have great flexibility in retrieving data. I don’t have to be restricted by just using keys. It’s also easy to pick up, since it’s a superset of SQL that SQL Server users will be comfortable with quickly. However, the tradeoff here is that indexing is important. Even more so than SQL Server indexing. If you were to write a query on the Name field, for instance, you should have an index like:
CREATE INDEX IX_Name ON `SocialMedia` (Name) USING GSI;Otherwise the query will fail to execute (if you have no indexing) or it will not be performant (if you only have a primary index created).
There are pros and cons in deciding to use referencing or not. The values in friends and user are similar to foreign keys, in that they reference another document. But there is no enforcement of values by Couchbase. The management of these keys must be handled properly by the application. Further, while Couchbase provides ACID transactions for single document operations, there is no multi-document ACID transaction available.
There are ways to deal with these caveats in your application layer that will be discussed further in later blog posts in this series, so stay tuned!
Key design and document differentiation
In relational databases, rows of data (typically, not always) correspond to a primary key, which is often an integer or a Guid, and sometimes a composite key. These keys don’t necessarily have any meaning: they are just used to identify a row within a table. For instance, two rows of data in two different tables may have the same key (an integer value of 123, for instance), but that doesn’t necessarily mean the data is related. This is because the schema enforced by relational databases often conveys meaning on its own (e.g. a table name).
In document databases like Couchbase, there isn’t anything equivalent to a table, per se. Each document in a bucket must have a unique key. But a bucket can have a variety of documents in it. Therefore, it’s often wise to come up with a way to differentiate documents within a bucket.
Meaningful keys
For instance, it’s entirely possible to have a FriendbookUser document with a key of 123, and an Update document with a key of 456. However, it might be wise to add some more semantic information to the key. Instead of 123, use a key of FriendbookUser::123. The benefits to putting semantic information in your key include:
-
Readability: At a glance, you can tell what a document is for.
-
Referenceability: If you have a
FriendbookUser::123document, then you could have another document with a keyFriendbookUser::123::Updatesthat has an implicit association.
If you plan on using N1QL, then you may not need keys to be this semantically meaningful. In terms of performance, the shorter the key is, the more of them can be stored in RAM. So only use this pattern if you plan on making heavy use of key/value operations instead of N1QL queries.
Discriminator fields
When using N1QL, another tactic that can be used in addition to or instead of meaningful keys is to add field(s) to a document that are used to differentiate the document. This is often implemented as a type field within a document.
{
"address" : "1800 Brown Rd",
"city" : "Groveport",
"state" : "OH",
"type" : "address"
}There’s nothing magical about the type field. It’s not a reserved word within a document and it’s not treated specially by Couchbase Server. It could just as easily be named documentType, theType, etc. But it can be useful within your application when using N1QL to query documents of a certain kind.
SELECT d.*
FROM `default` d
WHERE d.type = 'address'You may even take it a step further and add an embedded object to your documents to act as a kind of faux 'meta data':
{
"address" : "1800 Brown Rd",
"city" : "Groveport",
"state" : "OH",
"documentInfo" : {
"type" : "address",
"lastUpdated" : "1/29/2017 1:31:10 PM",
"lastUpdatedBy" : "mgroves"
}
}That may be overkill for some applications. It’s similar to a pattern I’ve seen in relational databases: a 'root' table to simulate inheritence within a relational database, or perhaps the same fields tacked on to every table.
Conclusion of part 1
This blog post covered data modeling using denormalization, data modeling using referencing, key design, and discriminating fields. Modeling data in a document database is a thought process, something of an art form, and not a mechanical process. There is no prescription on how to model your data in a document database: it depends greatly on how your application interacts with your data.
You can get the source code for the entire blog series on GitHub now, parts of which were featured in this blog post. If you have questions about various parts of that code, feel free to leave a comment below, or open an issue on GitHub.
Stay tuned for the next blog in the series, where data and data migration will be discussed.
If you have any questions, please leave a comment below, contact me on Twitter, or use the Couchbase Forums.
This is a repost that originally appeared on the Couchbase Blog: .NET Core List, Queue, and Dictionary Data Structures backed by Couchbase.
The addition of the sub-document API to Couchbase 4.5 has paved the way for efficient data structure support in Couchbase.
In this blog post, I’m going to show a demo of three types of data structures you can use with the Couchbase .NET SDK:
-
List - a list of objects, basically a List<T> backed by Couchbase
-
Queue - a queue of objects, basically a Queue<T> backed by Couchbase
-
Dictionary - a dictionary of objects, basically a Dictionary<K,T> backed by Couchbase
I’ll also discuss a little bit how this works behind the scenes.
You can play along at home if you like. The source code for this blog is available on GitHub, and Couchbase Server is free to download (developer previews of version 5 are currently available monthly).
List
A List<T> is a .NET data structure that is held in memory. With the data structures provided by the Couchbase .NET SDK, you can store it in a Couchbase document.
To create a Couchbase-backed List:
var list = new CouchbaseList<dynamic>(bucket, "myList");The string "myList" corresponds to the key for the document that will contain the list. When using CouchbaseList<T>, a single document with that key will be created (if one doesn’t exist already). If a document by that key already exists, CouchbaseList will use it.
You can now add/remove items from the list and that will all be persisted to the document. You can also perform other operations like getting a count of the items in the list.
// add 10 objects to the list
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++)
list.Add(new { num = i, foo = "bar" + Guid.NewGuid()});
// remove an item from the list by index
list.RemoveAt(5);
// show an item from the list by index
Console.WriteLine("5th item in the list: " + list[5].foo + " / " + list[5].num);The above code would result in a document with a key "myList" that looks like below. Notice that the item with num of 5 is not listed, because it was removed.
There’s something subtle in the above example that needs to be pointed out. Notice that I used var item = list[5]; and then item.foo and item.num in the WriteLine. If I used list[5].foo and list[5].num directly, that would result in two different subdocument calls to Couchbase. Not only is this less than optimal efficiency, but it’s possible for the values to change between the two calls.
[
{
"num": 0,
"foo": "bara1fd74ee-a790-4a0f-843c-abe449cb8b1d"
},
{
"num": 1,
"foo": "bardc1d8f9a-4e93-46f9-b8ae-ec036743869e"
},
{
"num": 2,
"foo": "bar9a60abe9-1e04-4fba-bd1f-f1ec39d69f56"
},
{
"num": 3,
"foo": "bar9566605b-7abf-4a0c-aa9d-63b98ce86274"
},
{
"num": 4,
"foo": "bar6261323f-de50-42a7-a8a7-6fcafb356deb"
},
{
"num": 6,
"foo": "bar13832bcb-2aa0-491a-a01f-1d496f999ffc"
},
// ... etc ...
]Queue
Very similar to List, you can create a Couchbase-backed queue:
var queue = new CouchbaseQueue<dynamic>(bucket, "myQueue");A queue is stored just like a list. The difference is that the ordering is significant, and this is reflected by the operations you perform on a queue: Enqueue and Dequeue.
for(var i = 0; i < 3; i++)
queue.Enqueue(new { num = i, foo = "baz" + Guid.NewGuid()});
// dequeue
var item = queue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine("item num " + item.num + " was dequeued. There are now " + queue.Count + " items left in the queue.");The above code would result in a document with a key "myQueue" (see JSON below). Notice there is no object in the array with num "0" because it was dequeued.
[
{
"num": 1,
"foo": "baz64bb62b6-bf23-4e52-b584-d2fa02accce6"
},
{
"num": 2,
"foo": "baz0a160bd9-aa7b-4c45-9e19-d1a3d982a554"
}
]Dictionary
Hopefully you’re seeing a pattern now. To create a dictionary:
var dict = new CouchbaseDictionary<string,dynamic>(bucket, "myDict");Again, a document will be created with the given key. The operations that can be performed include Add, Remove, and the indexer [] operation.
for(var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
dict.Add("key" + Guid.NewGuid(), new { num = i, foo = "qux" + Guid.NewGuid()} );
// print out keys in the dictionary
Console.WriteLine("There are " + dict.Keys.Count + " keys in the dictionary.");
foreach(var key in dict.Keys)
Console.WriteLine("key: " + key + ", value.num: " + dict[key].num);A dictionary document looks like:
{
"key5aa2520d-123c-4fca-b444-b0cb8846d46e": {
"num": 0,
"foo": "qux93b197dc-f175-4246-a38d-7b080eb9bea0"
},
"key55dee298-14c6-4da7-97a8-66c69d7e8a70": {
"num": 1,
"foo": "quxa593ee4c-682c-402d-887b-3f09f029e9b6"
},
"key3386afcf-7b70-4e4d-b9ae-6defbca33fe7": {
"num": 2,
"foo": "qux1259ae94-1008-4e1f-86a1-bfbd0873b09b"
},
"key2bc8c451-f125-4282-9fb4-7ea15f4b3168": {
"num": 3,
"foo": "qux1b6fb62b-9918-46dc-9a2f-610a55d017ef"
},
"key3f7041f3-abd3-49c7-a373-454cbd2ac0fc": {
"num": 4,
"foo": "qux0a87655f-197d-4fb2-8a54-b1de6e288de4"
}
}A note about C# dynamic: I used dynamic to keep the code samples short and simple. In your application, you are probably better off using a real defined C# type. It all gets serialized to JSON in Couchbase, of course.
Behind the scenes
Before the subdocument API was released in Couchbase Server 4.5, these data structures were possible, of course. The catch was that you would be loading up the entire document, putting it in a list, making changes to the list, and then saving the entire document. If you have large data structures, but are only reading or making changes to a single item, this would often result in wasted time and wasted bandwidth and possibly increased contention.
The subdocument-API (which you can use directly; I covered it in the Sub-document API in Couchbase Server 4.5 with the .NET SDK (revisited) blog post) is used behind the scenes in CouchbaseList, CouchbaseQueue, and CouchbaseDictionary. So when you add an item to a CouchbaseList, for instance, only that item is being sent over the wire, not the entire list.
Some operations will still need to get the entire document. For instance, iterating through a collection using a foreach loop will retrieve the full document. Removing an item from a list will result in the full document being scanned. But if sub-document operations come along in the future to support those actions, the SDK implementations will be updated accordinging.
Summary
These data structures are another tool to help you manage your data. Since they use the sub-document API, they are generally more performant than a whole-document approach. For more detail, check out the Data Structures documentation.
Have questions? Feedback? Need help? Please visit our forums, ping me on Twitter @mgroves, or leave a comment.
J. Tower is answering all my burning questions about .NET and .NET Core
Show Notes:
Want to be on the next episode? You can! All you need is the willingness to talk about something technical.
Theme music is "Crosscutting Concerns" by The Dirty Truckers, check out their music on Amazon or iTunes.
Steven Swenson is encrypting and hashing with .NET.
Show notes:
- Steven Swenson's blog
- Book: Cryptography Engineering, Design Principles and Practical Applications, by Bruce Schneier
- Adam Caudill
- Risky Business podcast
- libsodium crypto library
- Elliptic curve cryptography (ECC)
- CodeStock conference in Knoxville
- Azure Identity Services
- bcrypt is available on NuGet
- scrypt is available on GitHub and NuGet
Want to be on the next episode? You can! All you need is the willingness to talk about something technical.
Theme music is "Crosscutting Concerns" by The Dirty Truckers, check out their music on Amazon or iTunes.


